Container
- Container , is one of the most common and popular widget available in Flutter.
- You can think of a Container as a wrapper, which wraps other widgets.
- After wrapping your widget around the Container you can give a
color,padding,margin, etc. For example,Container( margin: const EdgeInsets.all(10.0), color: Colors.blue, width: 48.0, height: 48.0, ) - Output :

It's not required to have a child. We can create an empty container too.
- Let's discuss all the properties which are provided by the Container.
1. child :
- The child property of a Container allows us to place our own widget inside it so that we can decorate our widget easily. We can place any widget inside the child, for example
Text,Row,Column,Stacketc.Container( child: Text("Hello Container") ) - Output :

2. alignment :
- The alignment property will align the child of the container in 10 different ways.
topLeft,topCenter,topRight,centerLeft,center,centerRight,bottomLeft,bottomCenter,bottomRight
Container(
alignment: Alignment.bottomRight,
color: Colors.blue,
width: 150.0,
height: 100.0,
child: Text("Hello Container")
)
- Output :

3. color :
- color is another most common property of a container that is used to give the container background color.
- color takes color provided by the Colors class. There are mainly two Colors classes, Material and CupertinoColors class. We can use both of these classes to give color to the Container
Container( alignment: Alignment.bottomRight, color: CupertinoColors.activeGreen, // or Colors.green child: Text("Hello Container") )- Output :

4. constraints
- With constraints property we can tell the container to expand to fill a given sizes
- constraints takes BoxConstraints class as an input. There are many constructors available inside the BoxModel. Some of them are
tightForFinite,loose,tight,tightFor, etc. Container( constraints: BoxConstraints.tightForFinite(width: 200.0,height:100.0), alignment: Alignment.center, color: CupertinoColors.activeGreen, child: Text("Hello Container") )- The above code will create a box with constraints that require the given width or height. If no
widthorheightwere given then the constraints will be infinite, which means the box will take all the available space. - Output :

- The
looseconstraint is nothing but an axis with a minimum constraint of 0.0. It takesSize(width,height)as an input.Container( constraints: BoxConstraints.loose(Size(100.0,150.0)), ) 
You can define
maxWidth,maxHeight,minWidth,minHeightalso inBoxConstraintsconstructor.BoxConstraints( maxHeight: 100, maxWidth: 100, minHeight: 80, minWidth: 80 ),
5. decoration :
- decoration is a very cool property that provides tons of features for our box. Let's explore them.
- decoration takes
BoxDecorationconstructor as an input. This constructor provides a variety of ways to draw a box. - Box can have,
border,shadow,gradients,image,alignmentetc. Container( decoration: BoxDecoration( // Note: You can't have a property of "color" inside a container now as you've already defined in the decoration color:Colors.purple, borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(10.0), border:Border.all(color: Colors.red), boxShadow: [ BoxShadow( color: Colors.green, blurRadius: 5.0, spreadRadius: 5.0, ), ] ),
Now there are 4 more properties remaining of BoxDecoration i.e,
gradientandimage,backgroundBlendModeandshape. Let's see how to use them
Image :
Container(
decoration: BoxDecoration(
image:DecorationImage(image: NetworkImage("https://url.com/flutter-logo.png")),
border:Border.all(color:Colors.black),
gradient: LinearGradient(
colors: [
Colors.pinkAccent,
Colors.blueAccent
])
),
)

- Here in the
imageproperty you can pass other type of images likeAssetImageFileImage,MemoryImage,etc.
shape :
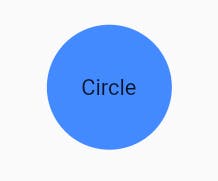
- You can make your container
circular,rectangular, or you can also specify thevalues` for custom shapes. - Example :
Container( decoration:BoxDecoration( color:Colors.blueAccent, shape: BoxShape.circle // or BoxShape.rectangle ), height:80.0, width: 120.0, child: Center(child:Text("Circle")), ),- Output :
backgroundBlendMode :
- Blend modes are used to determine how two layers are blended with each other.
- There are many blend modes available inside the BlendMode enum.
color,colorBurn,darken,difference,dst,hardLight, etc.- Example :
Container( decoration:BoxDecoration( backgroundBlendMode: BlendMode.difference, // or BlendMode.xor, BlendMode.darken etc color:Colors.blueAccent, shape: BoxShape.circle ), height:80.0, width: 120.0, child: Center( child: Text( "xor", style:TextStyle(color:Colors.white) ) ), ),- Output :
- Here I've displayed some of the
blendMode. Take a look. 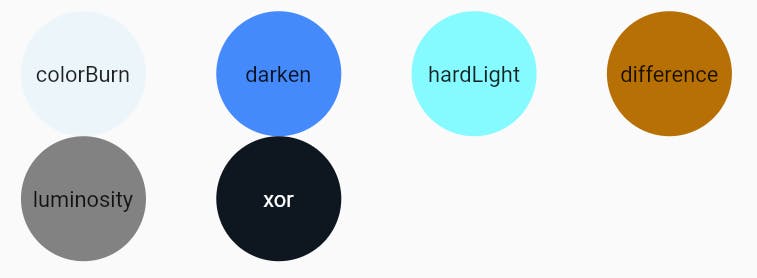
gradient:
- There are several types of gradients, represented by the various constructors in this class. LinearGradient, SweepGradient, RadialGradient,
LinearGradient() :
colors: List of colorsbegin: Offset at which the gradient is placed.end: Offset at which the gradient stops placed.stops: A list of values from 0.0 to 1.0 that denote fractions along the gradient- Example: as explained above
RadialGradient() :
- Same as LinearGradient, But this also takes properties like
radius,focal,tileMode,colors: List of colorsstops: A list of values from 0.0 to 1.0 that denote fractions along the gradient.focal: The focal point of the gradient. If specified, the gradient will appear to be focused along the vector from center to focal.focalRadius: The radius of the focal point of the gradient.radius: The radius of the gradient- Example :
Container( decoration: BoxDecoration( border: Border.all(color:Colors.black), gradient: RadialGradient( colors: [Colors.green, Colors.blue, Colors.orange, Colors.pink], stops: [0.2, 0.5, 0.7, 1], focal: Alignment(-0.1, 0.2), focalRadius: 1, radius: 0.1 ), ),SweepGradient() :
- Similar to Linear and Radial Gradient, however, takes two different properties i.e,
startAngle,endAnglestartAngle: The angle in radians at which stop 0.0 of the gradient is placed.endAngle: The angle in radians at which stop 1.0 of the gradient is placed.- Example :
Container( decoration: BoxDecoration( border: Border.all(color:Colors.black), gradient: SweepGradient( colors: [Colors.blue, Colors.green, Colors.yellow, Colors.red, Colors.blue], stops: [0.0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1], ), ), )- After applying
startAngleandendAngle
6. margin:
- Margin is used to create space around the widget
Container( color:Colors.teal, alignment: Alignment.center, width: 150.0, height: 100.0, margin: EdgeInsets.only(left:10.0) ) 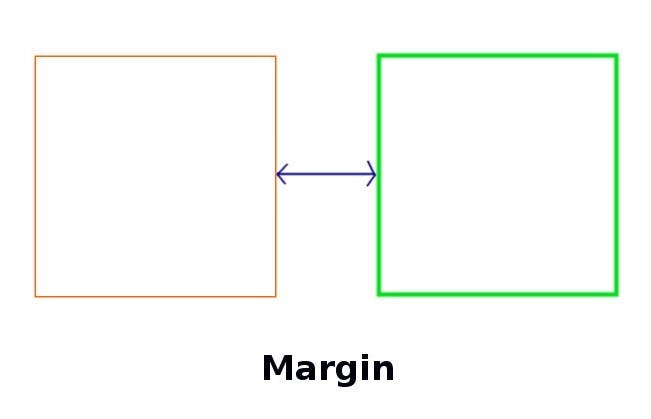
7. padding:
- Padding is used to create space from the inside of the widget
Container( color:Colors.teal, alignment: Alignment.center, width: 150.0, height: 100.0, padding: EdgeInsets.all(10.0) ) 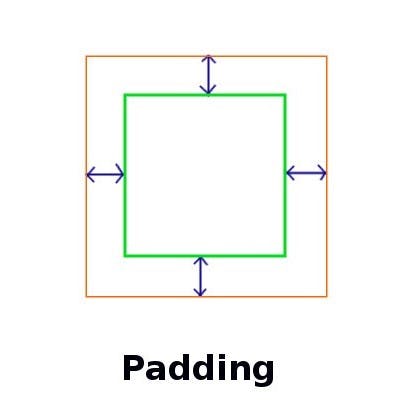
marginandpaddingtakesEdgeInsetsclass as an input.- The
EdgeInsetshas many constructor which is helpful to give margin/padding from different sides, some of them are: EdgeInsets.all(): To gives space from all the sides.EdgeInsets.only(): To give space from perticular side i.eleft,right,top,bottom.EdgeInsets.symmetric(): To give spacehorizontallyandvertically
8. transform:
- This is another cool property, which helps us to apply matrix transformation to paint our container/box as per our requirement.
- transform takes
Matrix4class, which has many useful constructor like,rotationX(),rotationY(),rotationZ(),skew(),translation(), etc - Example :
Container( transform: Matrix4.rotationZ(0.1), width:250.0, height:150.0, color:Colors.teal, child:Center( child:Text("Hello Container") ) )- Output :
- Similarly you can apply
rotationX(),rotationY(),rotationZ(),skew(),translation()properties to see cool changes
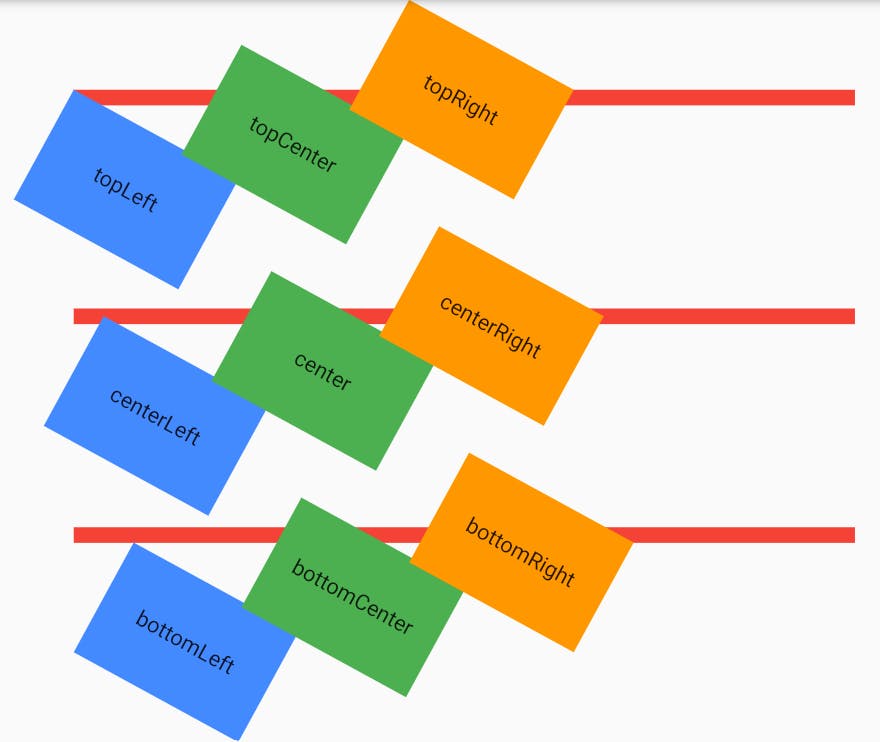
9. transformAlignment:
- This is an alignment of origin.
- Note that this alignment is relative to the size of the container.
- It will only work if
transformis specified. - The alignments are
topLeft,topCenter,topRight,centerLeft,center,centerRight,bottomLeft,bottomCenter,bottomRight. Container( height:80.0, width: 120.0, color:Colors.green, child: Center(child:Text("topCenter")), transform: Matrix4.rotationZ(0.5), transformAlignment: Alignment.topCenter, )- Below I've displayed all the possible alignment.
10. foregroundDecoration:
- This property will decorate the box from in front of the child.
- The
decorationproperty decorates/paints the box from behind the child. - Let's understand what do I meant by painting from the front of the child
- If we take the same snippet used in the
decorationexample, but instead of thedecorationI'm puttingforegroundDecoration.Container( foregroundDecoration: BoxDecoration( color:Colors.purple, borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(10.0), border:Border.all(color: Colors.red), boxShadow: [ BoxShadow( color: Colors.green, blurRadius: 5.0, spreadRadius: 5.0, ), ] ), child : //.... ), - Output :

- As we can see the
Textis not visible. It is because theforegroundDecorationhas painted the whole thing in front of our child widget.
- That's It. That's all you need to know about the Container.
- Thank you reading.