Object Oriented Programming in Dart: Inheritance
What is Inheritance in Dart? What are the types of Inheritance? What are the `extends` and `with` keywords and the differences between them?
In The Previous Article...
- First and foremost, welcome to the third article of this OOPs in Dart series. In the last post, we discussed a fundamental OOPs concept called Abstraction.
Where I described in depth what abstraction is and how it works using two simple examples.
Following that, we talked through Abstract Classes and Abstract Methods.
We also saw four rules/important factors to remember when using Abstraction. Then we discovered what Implicit Interface is in Dart. Finally, we looked at several Abstraction use scenarios.
All right, so in this article, we'll talk about Inheritance. Let's get started without further ado.
What is Inheritance 🤷🏻♂️?
- If we understand the meaning of Inheritance in simple English, It means
It is a process that involves the passing on of property from one generation to another, usually within the family, generally from older parents (donors) to their adult children (heirs). - And in Programming, Inheritance means :
When some class let's say Class B wants to access the properties/methods of some other class let's say Class A, then the process of accessing these properties is called Inheritance.
Example :
- Let's say we have a class named Shape. Which has one property called color. And a method that simply prints the total sides of that shape.
class Shape {
String? color;
void giveSides({required int noOfSide}){
print('$noOfSide Sides with $color Color');
}
}
- We have different types of shapes: Circles, Squares, Rectangles, etc. All can have different colors and sides.
- Now let's say we want to create a shape called Triangle.
class Triangle {}
- Now what we want is, we want this Triangle class to have all the properties which the Shape class has. How can we do that? Here comes the extends keyword.
extends Keyword
- To solve the above problem in dart we have a keyword called extends.
- As the name suggests it is used to extend something. We use this keyword when we want a class to have all the stuff defined in the other class. Let's put it to use.
- In our case we want the Triangle class to extend the Shape class.
class Triangle extends Shape {}
- Now, as soon as you do this, and then you create an Object of this Triangle class, you will get access to all the properties/methods defined in the Shape class.
class Shape {
String? color;
void giveSides({required int noOfSide}){
print('$noOfSide Sides with $color Color');
}
}
class Triangle extends Shape{}
void main() {
final triangle = Triangle();
triangle.color = 'Red';
triangle.giveSides(noOfSide: 3);
}
Console :
'3 Sides with Red Color'
- As you can see even if the property
colorand methodgiveSidesis not defined in the Triangle class, you are still able to use these. This is called Inheritance. You are inheriting all the stuff.
Base and Sub Class
- A class that inherits all the properties and methods is called Sub Class (Child Class) and a class that provides all these are known as Base class (Parent Class).
Types of Inheritance in Dart
- There are mainly 4 types of Inheritance. :
- Single-Level Inheritance
- Multi-Level Inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance
- Multiple Inheritance
Single-Level Inheritance
- In this type of Inheritance, a Single Class can extend the parent class.
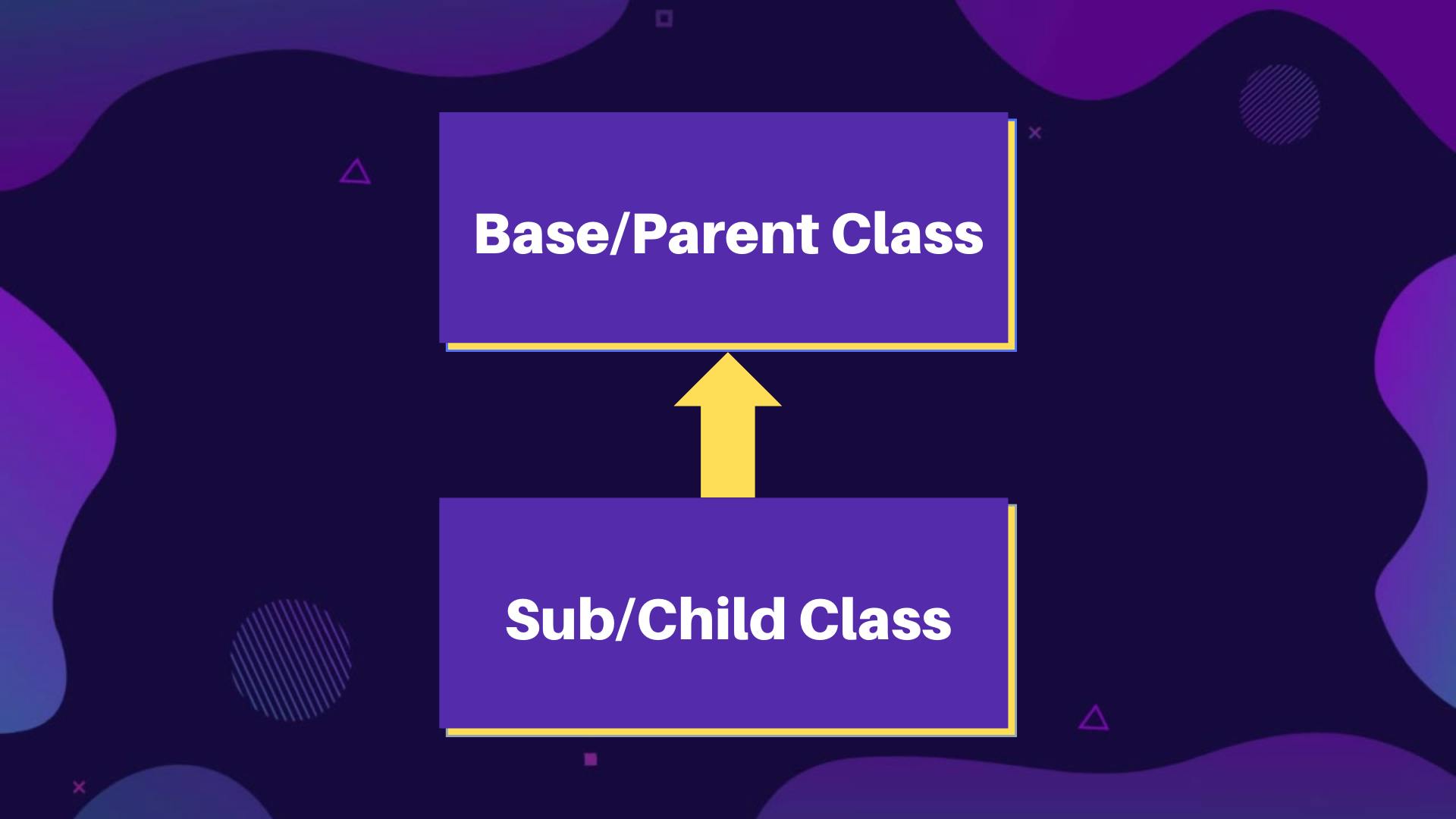
class Parent {}
class Child extends Parent {}
Multi-Level Inheritance
- As the name suggests, there will be some kind of chain of inheritance.
- For example, You got properties from your Father, and Your Father got some properties from your GrandFather :
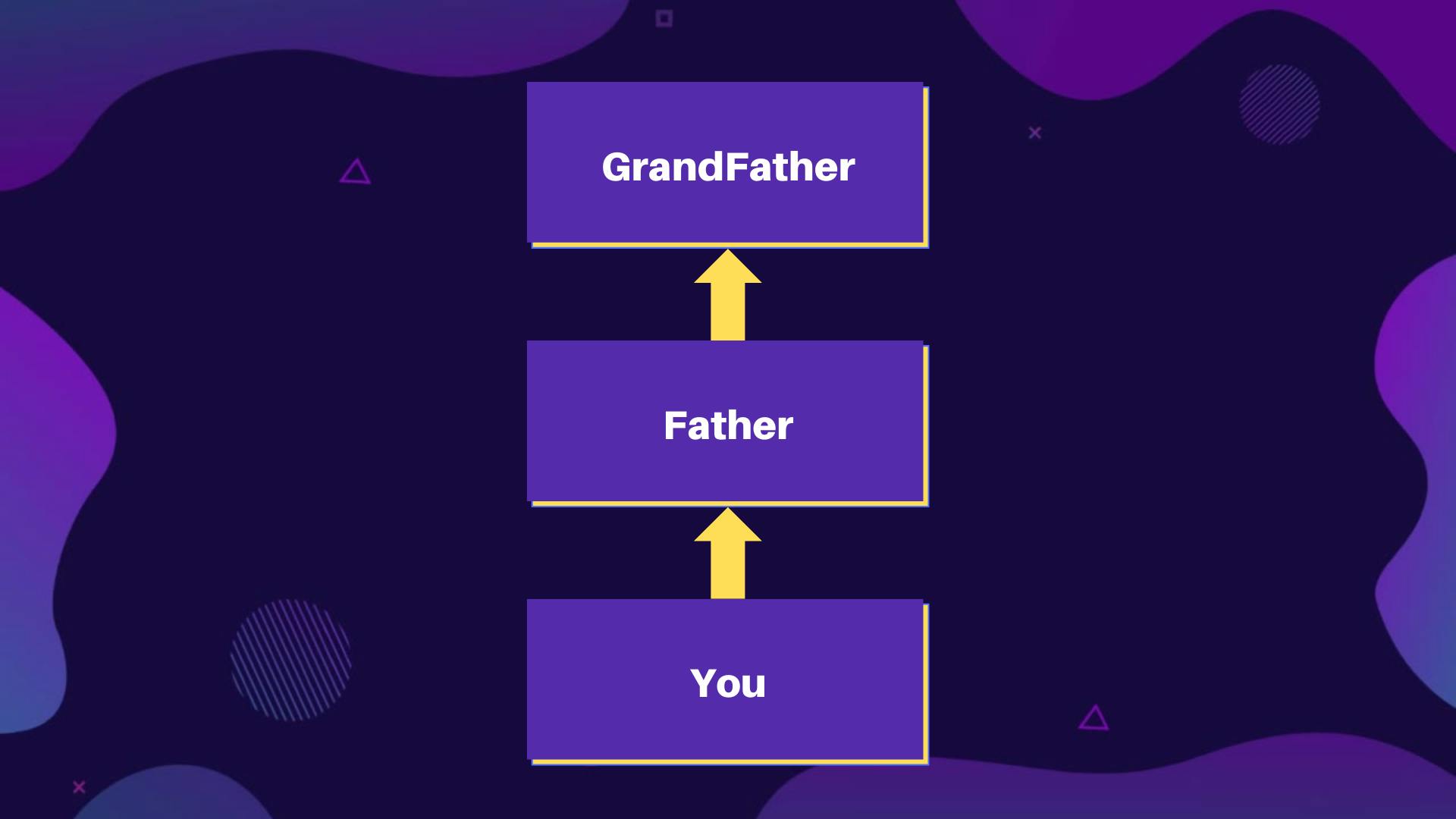
- In programming, one class extends some parent class and some other class extends the class which is extending that parent class.
- So, For example:
class A {}
class B extends A {}
class C extends B {} // and so on...
- If we notice the above syntax, we can clearly see that class A is the parent class for class B, which is extending it. Also, class B acts as a parent for class C, which is extending class B.
- Consider the following example :
class Shape {
String? color;
}
class Triangle extends Shape {
void area (int l, int h){
print(1/2*l*h);
}
}
class EquilateralTriangle extends Triangle {
// A triangle with equal sides
}
- As you can see, the Shape class acts as a Parent for Triangle class, on the other hand, the Triangle class acts as a Parent for EquilateralTriangle class. So, here class Triangle is acting as both Parent and Child class.
Hierarchical Inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance is an inheritance where more than one class inherits properties from a single Base class.
- For example :
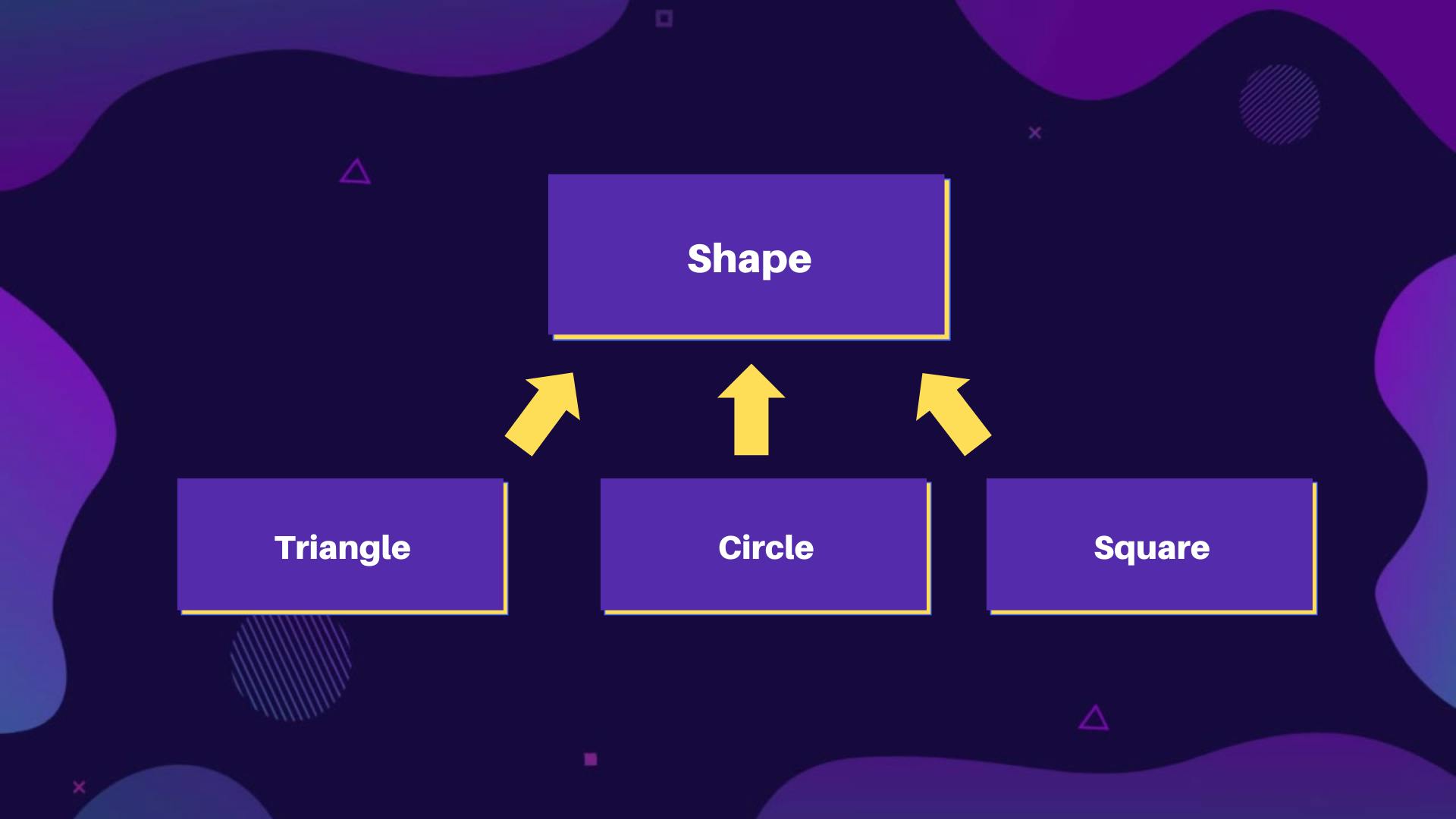
- In the above figure, as you can see all these three classes are extending the Base class Shape.
- If we put it in the code, it will be something like:
class Shape {
String? color;
void giveSides({required int noOfSide}){
print('$noOfSide Sides with $color Color');
}
}
class Triangle extends Shape {
void area (int l, int h){
print(1/2*l*h);
}
}
class Square extends Shape {
void area (int s){
print(s*s);
}
}
class Circle extends Shape {
void area (int radius){
print(3.14*radius*radius);
}
}
/* Shape
|
.---------.---------.
Triangle Square Circle
*/
Multiple Inheritance
- Multiple Inheritance is where a class can inherit from more than one class.
- Dart does not support Multiple Inheritance. Which means you cannot do like :
class A {}
class B {}
class C extends A,B{} // ❌
- But Dart does have a concept of mixins, which allows us to chain multiple classes.
mixins
- Mixins in Dart are a way of using the code of a class again in multiple class hierarchies. In other words, mixins are normal classes from which we can borrow methods(or variables).
- We make use of these mixins classes by using the with keyword followed by one or more mixins names.
Important points:
- Mixins Can't have Constructor
- You cannot use mixin if the parent class is extending some other class.
//* Point 1
mixins A {
A(); // ❌
}
//* Point 2
class A {}
class B extends A {}
class C with B {} // ❌ Because B is extending some other class
How can you achieve multiple inheritances using mixins?
- Well, if the class follows the 2 rules defined above you can extend more than one class using
withkeyword as shown below :
class A {}
class B {}
class C with A,B {}
- Let's consider our Shape example :
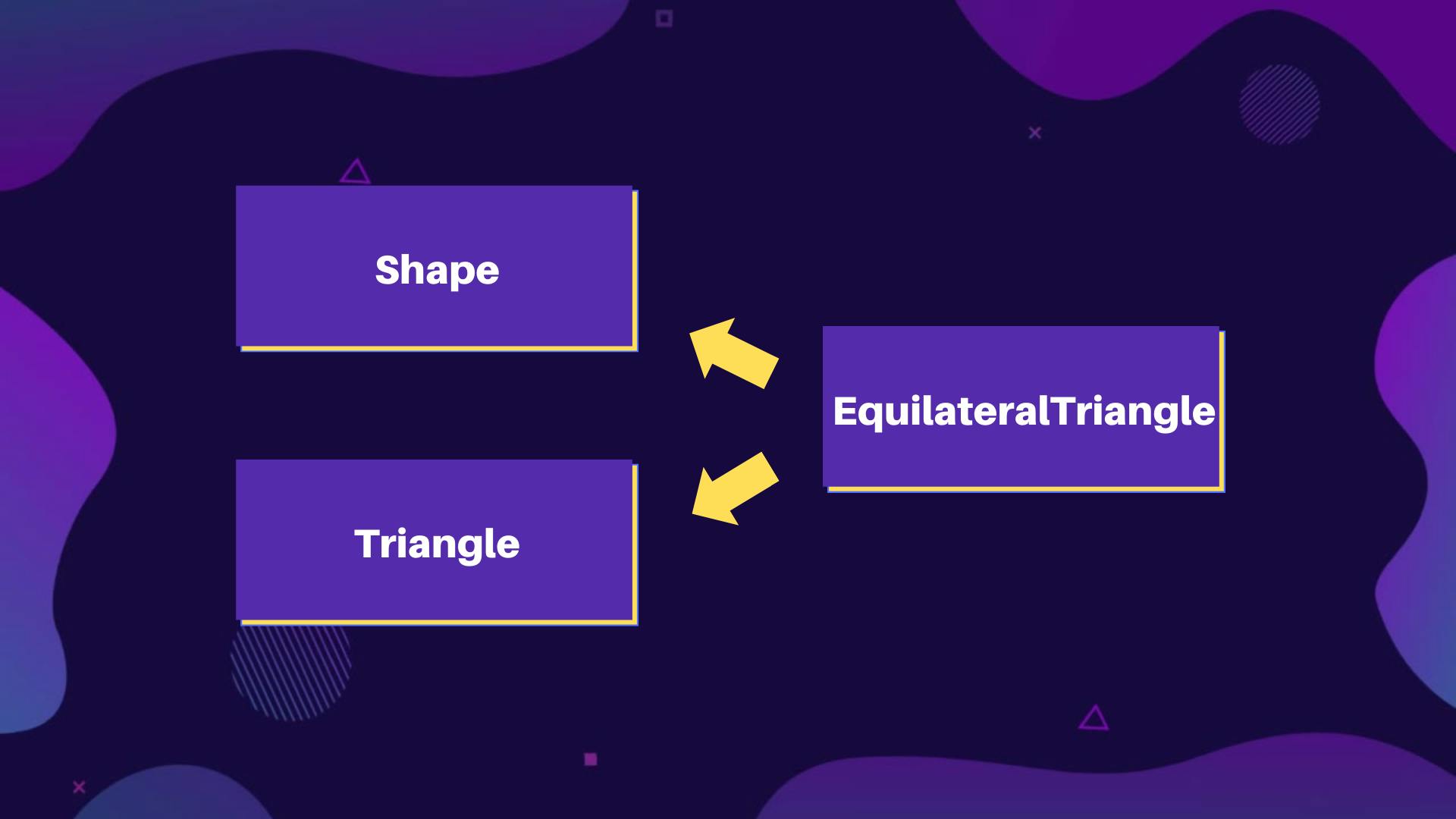
class Shape {
String? color;
}
class Triangle {
void area (int l, int h){
print(1/2*l*h);
}
}
class EquilateralTriangle with Shape, Triangle {
// A triangle with equal sides
}
void main() {
final equiTriangle = EquilateralTriangle();
equiTriangle.color = 'Red';
equiTriangle.area(1,2);
}
Difference between extends, with and implements
| extends | with | implements |
|---|---|---|
| Can inherit only one class | Can inherit multiple classes | Can inherit multiple classes |
| Not require to implement all the members | Not require to implement all the members | It Requires to implement all the memebers |
| Use this when you need to create a more specific version of a class. For instance, if Apple extends from the Fruit class (Example we saw in the previous article), it means all the properties, variables, and functions defined in the Fruit class will be available in the Apple class. | Use this when you want to extend multiple classes and also don't want to forcefully implement that classes' methods and properties | Use this when you want the class which inherits the type of the parent class. This means when you implement a class you are basically saying the MyClass looks like OtherClass. And you need to redefine all the methods and properties of that OtherClass |
Conclusion
- Inheritance is a very strong and useful concept of Dart. It helps to reduce code duplication and also cuts down on bugs.
- With the code written in the parent class, you no longer need to write the same code for multiple child classes that has the same properties.
- In this way, inheritance in dart implements code reusability to ensure better accessibility to users.
Wrapping Up
- I hope you enjoyed and learned something from this article. If you have any feedback/queries, leave them in the comments.
- Thank you for spending time reading this article. See you in the next article. Until then....


